VC Funding for Startups: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
VC funding for startups is a pivotal step in scaling a business and unlocking its growth potential. Starting and growing a startup is both challenging and exciting. While the initial stages, such as seed funding, lay the groundwork for success, securing Venture Capital (VC) funding becomes essential for navigating growth challenges. This funding provides startups with substantial financial support in exchange for equity, empowering them to expand operations, refine products, and compete in dynamic markets.
This comprehensive guide explores the latest insights into VC funding for startups in 2025, detailing the various funding stages, crucial factors to consider, and actionable strategies to secure VC investment effectively. Whether you’re a founder looking to scale or an entrepreneur seeking to understand the VC landscape, this guide has you covered.
What is VC Funding?
Venture capital (VC) is funding provided by investors to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. These investors, known as venture capitalists, typically offer capital in exchange for equity, meaning they take a percentage of ownership in the business. VC funding is essential for startups that have already passed the initial seed stage but need additional capital to scale, expand operations, and reach new markets.
VC funding is generally provided by specialized investment firms or high-net-worth individuals who pool their capital to invest in startups. While VC funding presents an opportunity for growth, it also carries high risk. Many startups face challenges in meeting the expected financial returns, and venture capitalists may lose their investments if the startup fails to deliver on its growth projections.
However, with the right strategies and a solid business model, startups can thrive and leverage VC funding to accelerate their growth.
The Stages of VC Funding in 2025
The process of securing VC funding typically involves multiple stages, each representing a different phase in the startup’s growth. In 2025, these stages have evolved, and entrepreneurs need to understand each phase to navigate the complexities of securing the right investment.

1. Seed Funding (Pre-VC Stage)
Before diving into VC funding, it’s important to understand seed funding, which is the initial investment a startup receives to develop its product, validate its market, and build its early-stage business operations. Seed funding often comes from angel investors or early-stage VC firms, and the amounts raised are typically smaller compared to later rounds.
At this stage, the startup usually has a proof of concept (PoC) or minimum viable product (MVP) and is focused on refining its offering to meet the needs of its target audience.
Key Considerations in Seed Funding:
- Investors look for a solid team and a compelling idea.
- The focus is on market research, customer validation, and product development.
- Seed funding amounts range from $100,000 to $2 million.
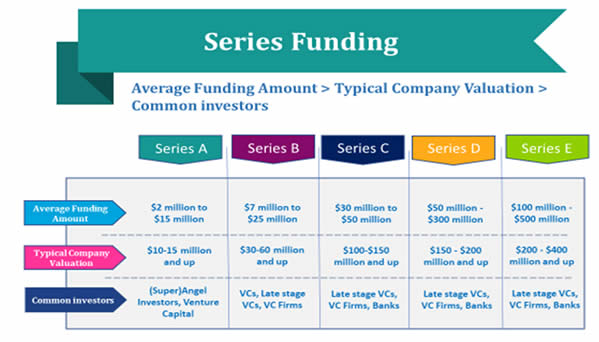
2. Series A Funding
Once a startup has successfully validated its business idea, built its MVP, and gained initial traction, it is ready to enter the Series A funding stage. This round is typically aimed at fueling growth and scaling the business. During Series A, startups need to demonstrate a clear product-market fit and provide evidence of strong demand for their offering.
In 2025, investors in Series A funding expect startups to have already achieved a stable customer base and be poised for rapid growth. The focus is on refining the product, improving user acquisition strategies, and increasing revenue generation.
Key Features of Series A Funding:
- Average funding amount: $2 million to $15 million.
- Typical company valuation: $10-15 million and up.
- Common investors: Venture capital firms, super angel investors.
How to Secure Series A Funding:
- Demonstrate product-market fit with a proven customer base.
- Show potential for significant revenue growth.
- Focus on scaling customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Optimize sales and marketing strategies for rapid growth.
3. Series B Funding
Series B funding comes when a startup has successfully scaled its operations and demonstrated its potential to grow further. This round focuses on expanding the startup’s market reach, improving its infrastructure, and further developing its product.
In 2025, startups that enter Series B funding are expected to have a solid track record of revenue generation and proven market demand. Investors at this stage are focused on driving business expansion, enhancing operational efficiency, and solidifying the startup’s competitive advantage.
Key Features of Series B Funding:
- Average funding amount: $7 million to $25 million.
- Typical company valuation: $30-60 million and up.
- Common investors: Venture capital firms, late-stage VCs.
How to Secure Series B Funding:
- Provide evidence of substantial revenue growth and strong business fundamentals.
- Focus on scaling operations and expanding into new markets.
- Hire a senior management team to drive business growth and improve operational efficiency.
- Explore mergers and acquisitions to enhance market positioning.
4. Series C Funding
Once a startup has achieved significant growth, the next stage is Series C funding. This round is meant to accelerate the business even further, often by expanding into new geographic regions or acquiring competitors to dominate the market.
In 2025, Series C investors are typically looking for startups that are already generating substantial revenue and have a proven ability to scale. At this stage, the company may be considering an Initial Public Offering (IPO) or large-scale strategic partnerships.
Key Features of Series C Funding:
- Average funding amount: $30 million – $50 million.
- Typical company valuation: $100-150 million and up.
- Common investors: Late-stage venture capitalists, institutional investors, banks.
How to Secure Series C Funding:
- Provide clear evidence of business stability and financial growth.
- Focus on scaling the business to new markets or achieving strategic acquisitions.
- Prepare for IPO or explore other exit strategies.
- Demonstrate a long-term vision for continued growth and market leadership.
5. Series D and Beyond
At this stage, most startups have either achieved significant success or are on the brink of scaling to the next level. However, some startups may choose to continue raising capital in Series D, E, or even beyond. These rounds are typically focused on market dominance, international expansion, or positioning the company for an IPO.
In 2025, Series D and beyond rounds often come with higher valuations and larger funding amounts, reflecting the lower risk associated with a startup’s proven success and track record.
Key Features of Series D and Beyond:
- Average funding amount: $50 million to $300 million or more.
- Typical company valuation: $150-400 million and up.
- Common investors: Late-stage VCs, institutional investors, private equity firms.
How to Secure Series D or E Funding:
- Ensure your startup has a solid growth trajectory and proven financial performance.
- Use the funds to build out new products, explore new markets, or execute a large-scale acquisition.
- Prepare for an IPO or other exit strategies that increase valuation.
Challenges and Considerations for Securing VC Funding in 2025
While securing VC funding can provide significant growth opportunities, startups face challenges that need to be addressed before seeking funding. Investors are highly selective in 2025, and startups must demonstrate strong leadership, clear market demand, and scalability to succeed in the competitive VC environment.
Key Considerations for Securing VC Funding:
- Understand Investor Needs: Conduct thorough research to understand the requirements and preferences of potential investors. Each VC firm has a unique focus, so tailor your pitch accordingly.
- Be Transparent About Risks: Investors appreciate transparency. While they expect high returns, they also want to understand the risks involved in your startup’s journey.
- Have a Strong Team: A well-rounded and capable team is crucial. Investors want to know that your team has the expertise to execute the business plan.
- Have a Scalable Business Model: VCs are interested in startups with a scalable business model that can generate significant returns.
- Know Your Numbers: Be prepared to present detailed financial projections, including revenue, expenses, and profitability. Investors want to understand your financial trajectory and how you plan to use their funds.
The Role of Angel Investors in Bridging the Gap
Although venture capital is a crucial source of funding for many startups, angel investors continue to play a significant role, especially in the early stages. In some cases, angel investors can help bridge the gap between seed funding and larger VC rounds, providing the necessary capital to meet growth targets and secure additional funding from venture capital firms.
Conclusion: VC Funding for Startups
VC funding remains a critical lifeline for startups looking to scale and achieve long-term success. In 2025, the landscape for venture capital investment continues to evolve, with different stages of funding designed to support startups at various growth points. From Series A to Series D and beyond, startups must carefully plan their funding strategy and focus on demonstrating traction, scalability, and a strong business model to attract investors.
With a clear understanding of VC funding stages and the requirements for securing investment, entrepreneurs can confidently navigate the challenges of scaling their startups and positioning themselves for success in the competitive world of venture capital.
About CO-OFFIZ : Coworking Space in Delhi-NCR
Co-Offiz is a leading provider of coworking spaces in Delhi-NCR tailored for young professionals, startups, freelancers, and entrepreneurs. We emphasize a collaborative work culture that enhances productivity while providing a hassle-free and aesthetically pleasing environment based on Vastu principles.
Our modern amenities include high-speed internet, unlimited tea/coffee, breakout zones, power backup, and CCTV security. Our vibrant meeting rooms feature LED TV projectors and ergonomic chairs, fostering an ideal workspace.
With locations in Preet Vihar (East Delhi), Janakpuri (West Delhi), Netaji Subhash Place (North Delhi), Noida Sec-63 and Gurugram Sec-58, we offer flexible seating, dedicated desks, and private cabins at competitive prices, all conveniently located near metro stations for easy access.